Overview
Aortic Dissection
An aortic dissection occurs when the innermost layer of the aorta tears. This tear creates an "false" path that lets blood enter between the layers of the aorta. The false path leads to poor blood flow and can cause the aorta to bulge (aneurysm) or rupture.
If blood is not flowing through your aorta properly, it may not flow to the rest of your body like it should. This can damage your organs and parts of your body. An aortic dissection can happen suddenly (acute) or be present for years (chronic).
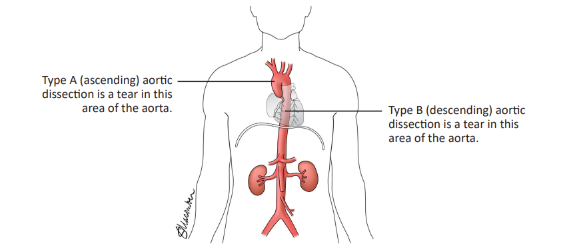
Aortic dissection starts as a tear in the aortic wall. Blood flows into a false passage and can then flow throughout the entire aorta.

